How Does Cenobamate Compare with Third-Generation Anti-Seizure Medications in Terms of Cost-Effectiveness?
The main goal of epilepsy treatment is to achieve seizure freedom without unacceptable side effects of therapy. Despite the benefits of the latest generation of anti-seizure medications (ASMs), approximately 40% of patients suffer from drug-resistant epilepsy. The recently approved cenobamate brings new hope to patients. A Spanish pharmacoeconomic study aimed to compare the cost-effectiveness of cenobamate with selected third-generation ASMs as adjunctive therapy in patients with drug-resistant focal epilepsy.
Anti-Seizure Treatment in Patients with Focal Seizures
In the past decade, several third-generation ASMs (brivaracetam, perampanel, lacosamide, and eslicarbazepine acetate) have been approved. These active substances were administered to patients with drug-resistant epilepsy (DRE) during their clinical development and are now commonly used for this indication. Third-generation ASMs are considered better-tolerated medications with fewer drug interactions. However, their introduction into the market has not significantly increased the probability of achieving seizure freedom, which remains at approximately 4%.
Cenobamate is an ASM approved by the European Medicines Agency (EMA) as an adjunctive treatment for adult patients with focal seizures, with or without secondary generalization, who have not achieved adequate disease control despite previous therapy with at least two anti-epileptic drugs. For the sustainability of the healthcare system, it is necessary to assess the relative clinical benefit of a new drug compared to established practices once it is introduced to the market. This was the aim of the authors of the presented analysis from the Spanish clinical practice.
How to Assess the Cost/Effectiveness Ratio?
A simple way to evaluate the clinical benefit of a treatment is the NNT (number needed to treat) parameter. It quantifies the number of patients that need to be treated to achieve one additional study goal (e.g., seizure freedom in one patient or preventing one death). The cost-effectiveness is then indicated by a similar parameter, CNT (cost needed to treat).
Study Methodology
The NNT and CNT were calculated concerning the achievement of a 50% reduction in seizures (≥50% response rate), or complete seizure freedom (100% response rate) in pivotal clinical trials of cenobamate, brivaracetam, perampanel, lacosamide, and eslicarbazepine acetate. The NNT was defined as the reciprocal difference between the response rate of the treatment and the placebo response rate, depending on different dosages (minimum, medium-defined, and maximum daily dosage). The CNT was determined by multiplying the NNT by the cost of annual therapy.
Results
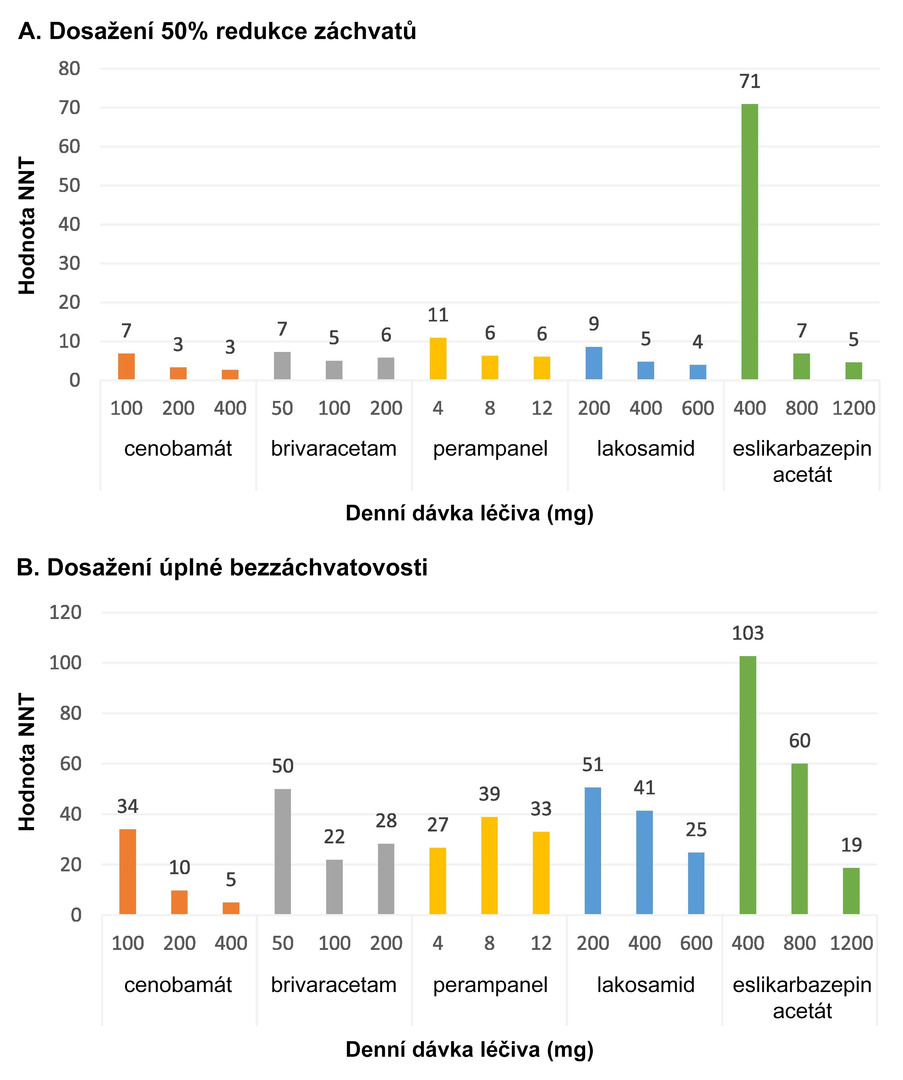
Cenobamate therapy was associated with the lowest NNT values regardless of the dosage, both for achieving a 50% reduction in seizures and for seizure freedom (see Fig. 1).
Fig. 1 NNT values of the evaluated ASMs according to the dosages used
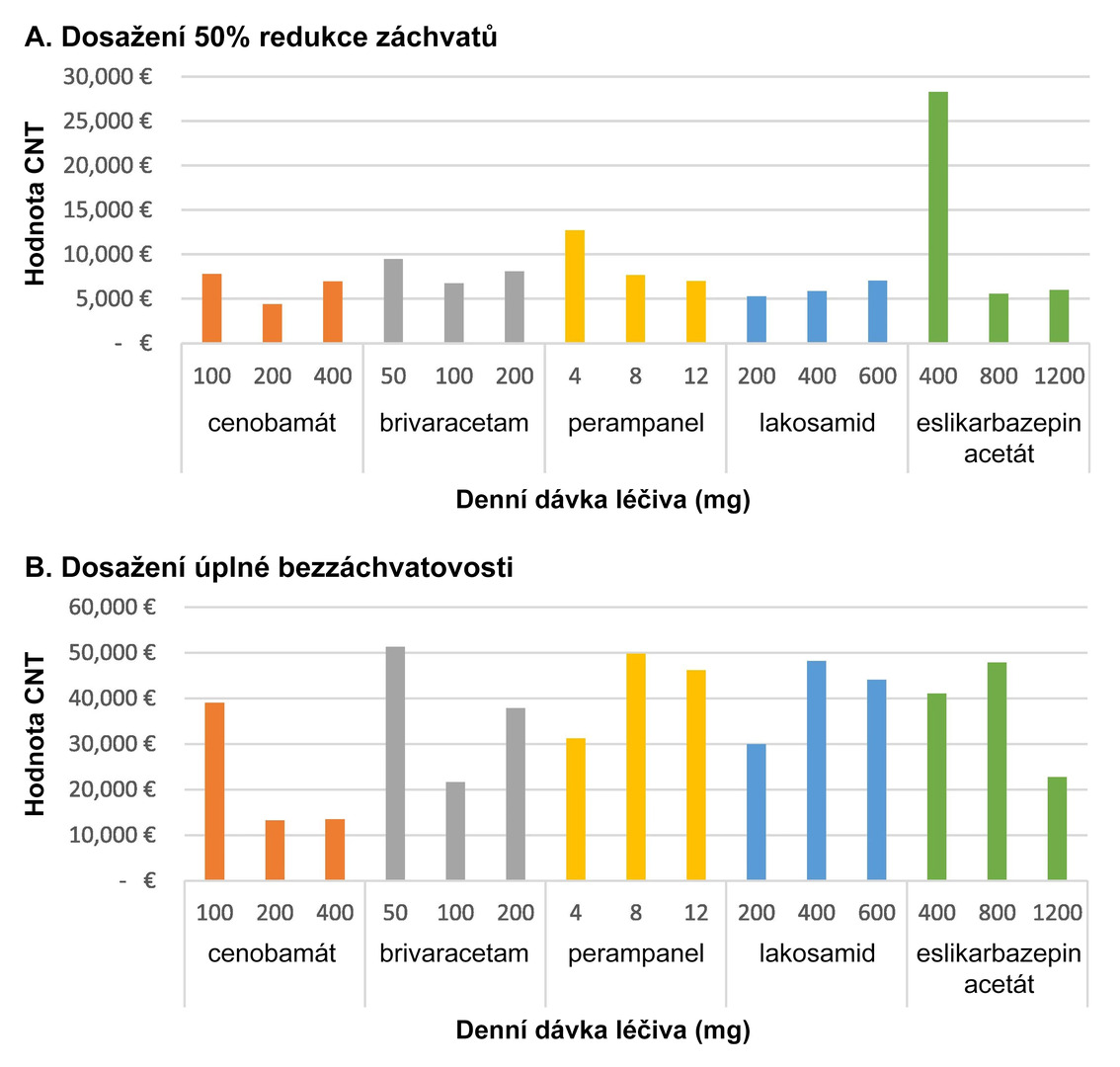
For achieving a ≥50% response rate, cenobamate therapy was associated with the lowest costs within defined daily doses; lacosamide was the most cost-effective at minimal doses, and eslicarbazepine acetate at maximum dosing. For achieving seizure freedom, the costs were lowest with cenobamate across the range of defined daily doses and maximum doses, and with lacosamide at minimal doses (see Fig. 2).
Fig. 2 Annual CNT values of the evaluated ASMs depending on the dosage used
Conclusion
Compared to other third-generation ASMs, cenobamate could represent the most effective anti-seizure treatment across all dose ranges. Within defined daily doses, it was also the most cost-effective therapy, both in terms of reducing seizure frequency by at least 50% and achieving complete seizure freedom.
(este)
Sources:
1. Villanueva V., Serratosa J. M., Toledo M. et al. Number needed to treat and associated cost analysis of cenobamate versus third-generation anti-seizure medications for the treatment of focal-onset seizures in patients with drug-resistant epilepsy in Spain. Epilepsy Behav 2023 Feb; 139 : 109054, doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2022.109054.
2. SPC Ontozry. Available at: www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/ontozry-epar-product-information_cs.pdf
Did you like this article? Would you like to comment on it? Write to us. We are interested in your opinion. We will not publish it, but we will gladly answer you.
